
Maintaining a healthy gut is essential for overall well-being, as it plays a crucial role in digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune function. Probiotics and prebiotics are two vital components that contribute significantly to gut health. In this article, we will explore five key benefits of them in promoting gut health.
1. Improved Digestion and Nutrient Absorption

Probiotics and prebiotics work together to enhance the digestive process. Probiotics help break down complex food compounds and convert them into easily absorbable nutrients. They also produce enzymes that aid in the digestion of certain foods, such as lactose in dairy products.
On the other hand, prebiotics serve as food for probiotics, stimulating their growth and activity. By nourishing these beneficial bacteria, prebiotics create an environment in which probiotics can thrive and effectively aid in the digestion and absorption of nutrients.
2. Enhanced Immune Function
A robust gut microbiome is closely linked to a strong immune system. Probiotics play a pivotal role in regulating the immune response by promoting the production of antibodies and enhancing the activity of immune cells. They also help prevent harmful pathogens from colonizing the gut lining, reducing the risk of infections and immune-related disorders.
Prebiotics, by supporting the growth of probiotics, indirectly contribute to a well-functioning immune system. A balanced gut microbiome, thanks to the synergistic action of probiotics and prebiotics, helps in defending the body against harmful invaders and maintaining overall health.
3. Reduction of Digestive Disorders
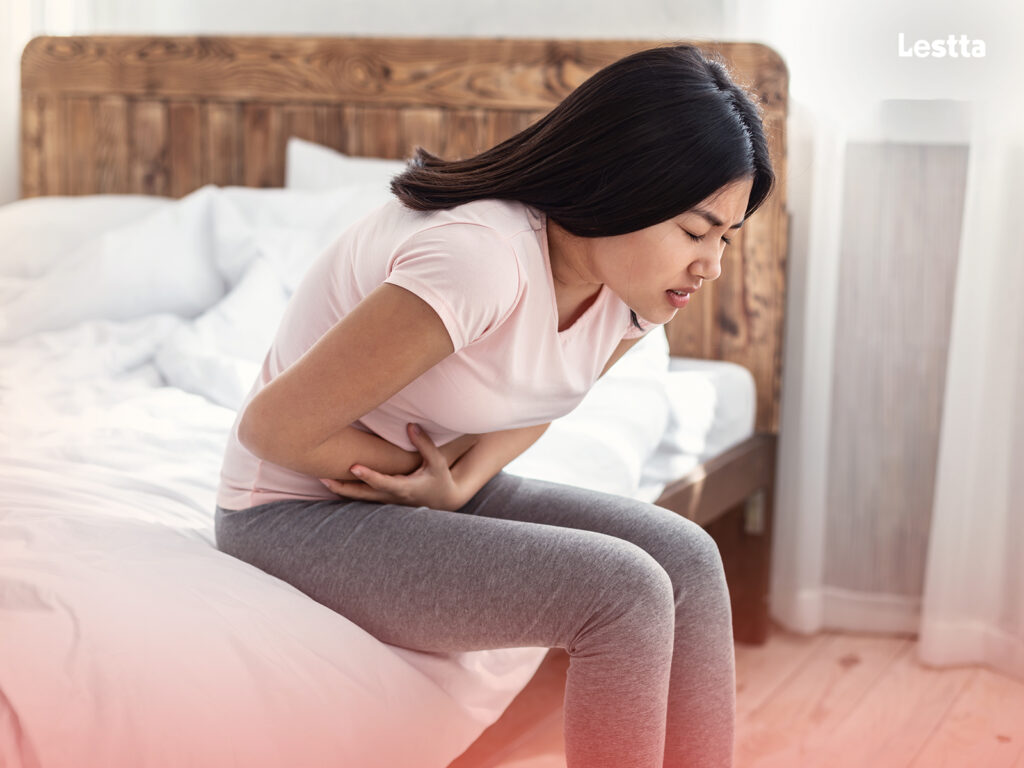

Digestive disorders, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and constipation, can significantly impact one’s quality of life. Fortunately, probiotics and prebiotics offer promising solutions. Studies have shown that probiotics can alleviate symptoms of IBS, including bloating, abdominal pain, and irregular bowel movements.
The beneficial bacteria in probiotics can restore the gut’s microbial balance and reduce inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. Prebiotics, by encouraging the growth of these beneficial bacteria, help in maintaining a balanced gut ecosystem, which can alleviate symptoms and prevent the recurrence of digestive disorders.
4. Management of Weight and Metabolism

The gut microbiome influences various aspects of metabolic health, including weight management and blood sugar control. Probiotics have been associated with a reduced risk of obesity and metabolic disorders by modulating the gut microbiota’s composition.
Certain probiotics can increase the production of hormones that promote satiety, leading to better appetite regulation and potentially aiding weight loss efforts. Prebiotics, by fostering the growth of probiotics, can indirectly influence metabolic health by improving the gut’s ability to extract energy from food and regulating insulin sensitivity.
5. Mental Health and Well-being

The gut-brain axis is a complex communication network between the gut and the brain. Emerging research suggests that probiotics and prebiotics may positively influence mental health and emotional well-being.
Probiotics can produce neurotransmitters like serotonin, which plays a vital role in regulating mood and emotions. Additionally, the gut microbiome’s balance is linked to the body’s stress response, and probiotics may help mitigate stress and anxiety. Prebiotics, as the fuel for probiotics, can indirectly contribute to mental health by fostering a healthy gut environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the benefits of probiotics and prebiotics in gut health are undeniable. From improving digestion and nutrient absorption to bolstering immune function, managing weight, and enhancing mental well-being, these two components play a crucial role in maintaining a thriving gut ecosystem.









