
Salt substitutes have gained popularity as a seemingly healthier alternative to traditional table salt. Promoted as a way to reduce sodium intake and manage blood pressure, these substitutes claim to provide the same taste while being better for our health.
However, it’s crucial to be aware of the potential risks of salt substitutes. In this article, we will explore seven dangers that you must know to make informed decisions about your diet and overall well-being.
1. Excessive Potassium Intake
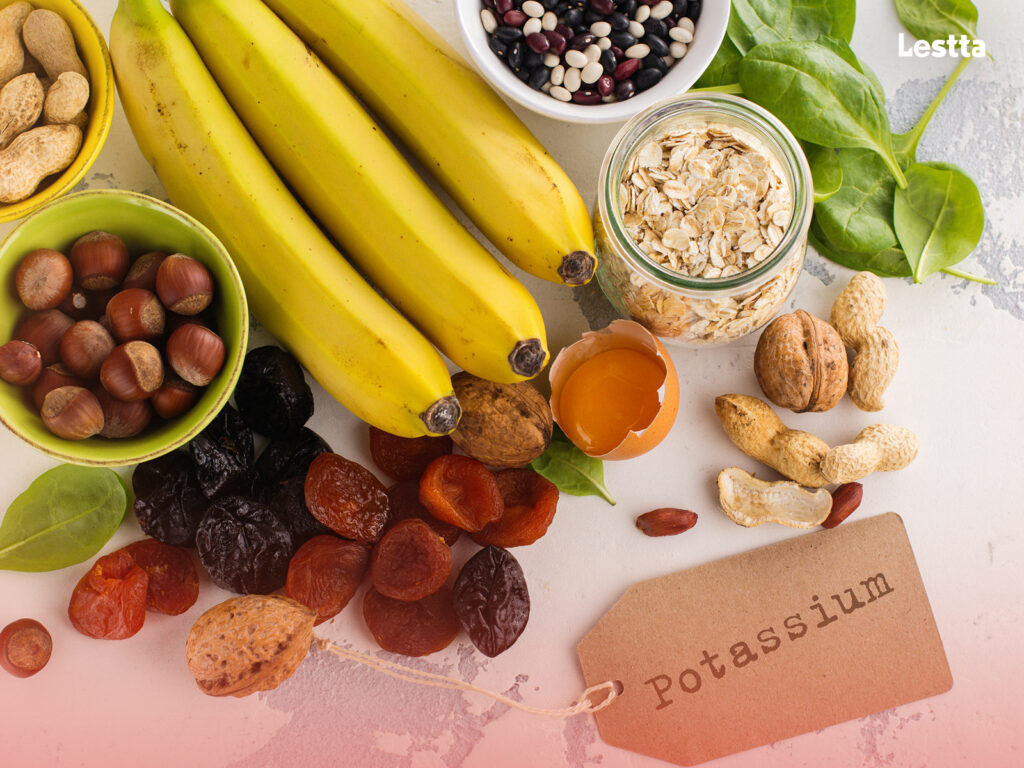

Many salt substitutes contain potassium chloride as a key ingredient. While potassium is an essential mineral, excessive intake can be harmful, particularly for individuals with kidney problems or those taking medications that affect potassium levels.
Consuming too much potassium can lead to an imbalance in electrolytes, causing irregular heart rhythms and muscle weakness.
2. Medication Interactions
Salt substitutes can interact with certain medications, including those prescribed for hypertension, diabetes, and kidney diseases. Potassium-based substitutes can interfere with the effectiveness of medications or cause unwanted side effects. It is vital to consult with a healthcare professional before using salt substitutes if you are taking any medications.
3. Allergic Reactions
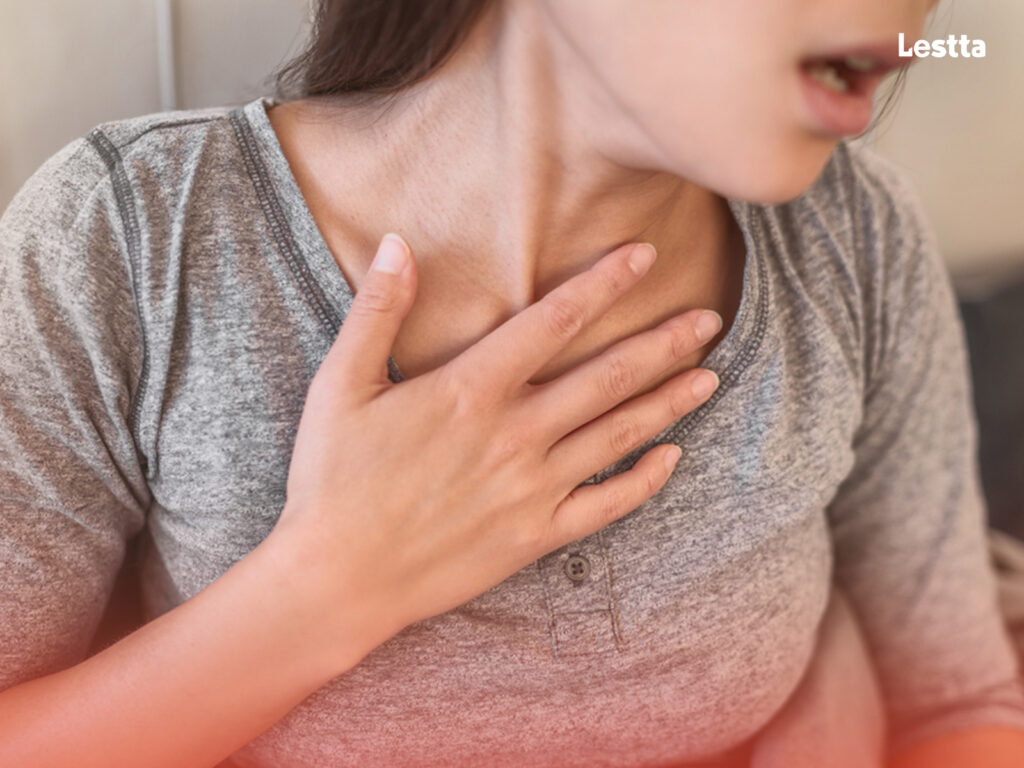

Some individuals may be allergic to certain ingredients present in salt substitutes. People find common allergens like soy, gluten, or artificial additives in these products. Allergic reactions can range from mild symptoms like hives and itching to severe reactions like difficulty breathing or anaphylaxis.
Reading ingredient labels and being aware of any known allergies is crucial when considering salt substitutes.
4. Mineral Imbalances
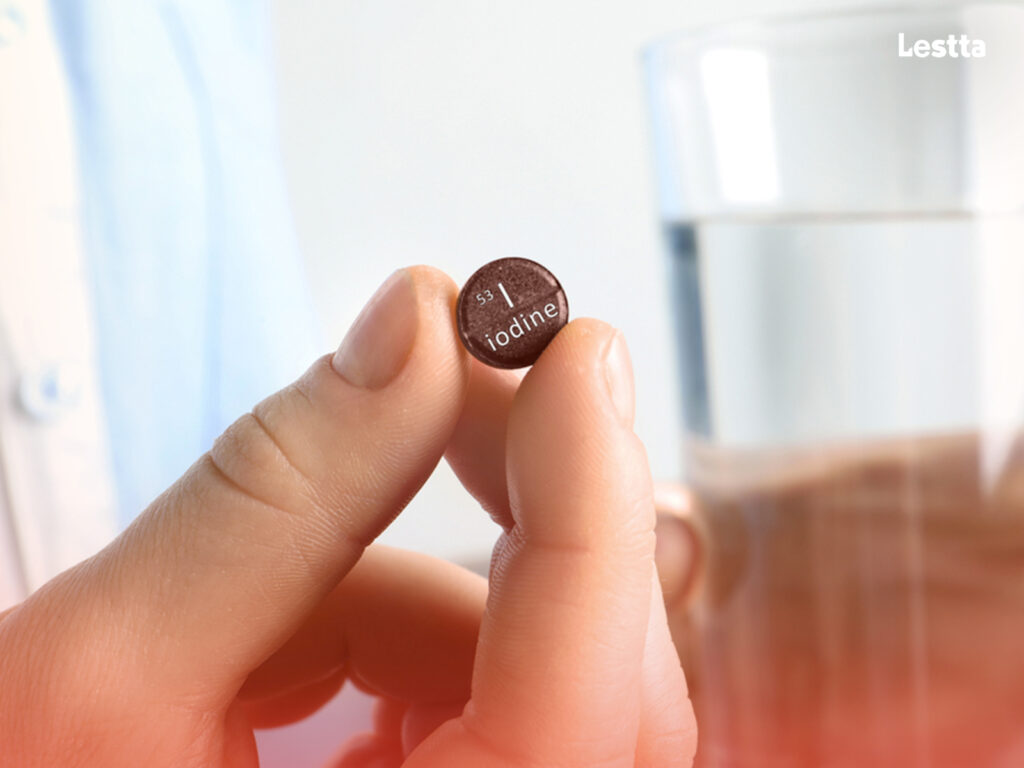

Salt substitutes often lack iodine, an essential mineral for thyroid function. Insufficient iodine intake can lead to thyroid disorders, affecting metabolism, energy levels, and overall health.
It is crucial to ensure adequate iodine consumption through alternative dietary sources like seafood, dairy products, or iodized salt.
5. Bitter Taste and Palatability

Salt substitutes may have a bitter taste or an aftertaste that can be unpleasant for some individuals. This can lead to dissatisfaction with food and reduced enjoyment of meals.
As a result, people may compensate by adding more salt or seeking high-sodium processed foods, ultimately defeating the purpose of using a salt substitute.
6. Psychological Impact

For individuals who are accustomed to the taste of regular salt, switching to a salt substitute can be challenging. The psychological aspect of taste and satisfaction cannot be overlooked.
The dissatisfaction caused by the taste difference might lead to a higher likelihood of abandoning the use of salt substitutes altogether and returning to excessive sodium intake.
7. Misleading Marketing Claims

While salt substitutes are marketed as healthier alternatives, it’s essential to scrutinize their claims. Some products may be low in sodium but contain other harmful additives or excessive amounts of potassium.
Always read product labels carefully and choose reputable brands to ensure you are making an informed choice.
Conclusion
While reducing sodium intake is beneficial for many individuals, it’s important to be aware of the potential dangers associated with salt substitutes. Excessive potassium intake, medication interactions, allergic reactions, mineral imbalances, palatability issues, psychological impact, and misleading marketing claims are some of the risks to consider.
It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes and to explore other strategies for reducing sodium intake that align with your individual health needs. Remember, informed decisions about your diet are key to maintaining a balanced and healthy lifestyle.









